When you search for "content writers" on LinkedIn, you're bound to come across an incredibly diverse range of professionals.
For instance, you'll see some content writers create social media copy for small businesses, while others write press materials for insurance brands.
You'll also find that some content writers write long-form editorial content for glamorous magazines, while the more entrepreneurial-type write scripts for their own branded content, like podcast or video.
So, what's going on here ... Are some of them lying?
In fact, they're all telling the truth. Content writing can take various forms, but in essence, it comes down to creating content for digital formats — and (at least in our case) for marketing purposes.
Here, we'll explore what content writing is (hint, hint … I'm currently doing it), as well as tips to take your own content to the next level. Plus, we'll explore examples of incredible, high-quality content writing.
But, to start — What is content writing, anyway?
What is content writing?
Content writing is the process of writing, editing, and publishing content in a digital format.
That content can include blog posts, video or podcast scripts, ebooks or whitepapers, press releases, product category descriptions, landing page or social media copy ... and more.
Simply put, content writers are the storytellers for their brand. They convey meaningful, helpful, and insightful messages to inspire and move an audience to take action — that action being a final sale.
Nowadays, content creation is a critical component of most businesses marketing strategies — in fact, as of 2020, 70% of marketers now actively invest in content marketing.
This means the role of content writer is more in-demand than ever before. However, the role varies depending on both industry and business needs.
For instance, some businesses might invest heavily in a social media strategy, while other companies prefer creating content in the format of blog posts or e-books.
Regardless of format, a content writer is critical for creating high-quality content that represents and strengthens a brand's voice, while attracting, engaging, and delighting the right audience.
When done right, content writing has the power to convert readers into prospects, and prospects into paying customers. So it's undeniably important for your business' bottom-line that you're able to consistently create helpful, engaging content.
But that's easier said than done. To help take your content to the next level, let's dive into some of my favorite content writing tips (these have personally helped me, as well).
12 Content Writing Tips
1. Write unique and original content, and go above-and-beyond what you find online.
Whenever I start a new blog post, like this one, I start with plenty of online research — but that's not where it ends.
After Googling relevant topics, including "content writing tips", I begin creating an outline using some of the information I find online.
However, your piece will never rank if you just copy-and-paste the same information that already exists online — and, even if it does, when your readers catch on (and they will), they'll lose trust in your brand as an authority within the industry.
Once I finish my rough outline (which will include about 60% of the information I found through online research), I fill in the remaining 40% with unique, original insights. If I know about a topic personally (as is the case with "content writing", since I'm a content writer myself), I'll fill in the outline with original anecdotes, tips, or personal examples.
However, if I don't know much about the topic at-hand, that doesn't mean I simply use what's already online. Instead, I'll reach out to internal HubSpotters who are experts on the topic or use other original internal-company resources, or I'll conduct external outreach via my social networks to find a reputable source willing to provide tips, quotes, or original examples to beef up my piece.
Additionally, I'll look for content regarding the topic across a wide range of sources — including YouTube, LinkedIn, Reddit, Quora, as well as podcasts — to ensure when readers' come across my content, it's both comprehensive and unique.
If they can find the same information elsewhere on Google, why should they stay on your page? As a good content writer, it's your job to take your content to the next level, always.
2. Write a good hook to grab your reader's attention.
Sometimes, it's easy to write a good hook — particularly if the topic is intriguing or exciting to you, as the writer.
But what about more boring, mundane topics, like Rel=nofollow?
In certain cases, writing a good hook requires pulling back and looking at the bigger picture. For instance, while rel=nofollow isn't the most fascinating topic (in my opinion), what is interesting to me is SEO, and how SEO can directly impact a company's ability to reach new audiences — plus, how Google has needed to change regulations in recent years due to an increase in illegitimate sites.
Which means, when I started writing 3 Reasons Why SEO's Are Upset About Google's Rel=nofollow Announcement, I used that angle to inspire my hook, and painted a picture: Myself as a Wikipedia editor, writing about zebras, and getting paid $500 to link to a fake news website.
(Now you're interested, aren't you?)
My Creative Writing background helps in this case, and I'm willing to bet your own passion for writing will help you create exciting hooks, as well.
Oftentimes, the introduction and hook is your best opportunity to use your writing skills to truly inspire, move, surprise, and delight your readers from the get-go. Take advantage of that space by thinking: What would make me and my friends want to keep reading?
3. SEO-optimize your content for search engines.
Your writing can be absolutely stunning, but if it's not SEO-optimized, no one will ever read it.
As a content writer, it's critical you become familiar with SEO when it comes to writing.
Being an SEO-savvy writer can help you ensure your content ranks on whichever platforms you're publishing, including YouTube, Google, or even social sites like Instagram.
Plus, you can use SEO to ensure you're writing about the most popular topics related to your products or services, and covering the right sub-topics when you're writing about a given topic.
For instance, "content writing tips" is a keyword phrase I found when conducting keyword research on the topic of "content writing" as a whole — it's not necessarily a sub-topic I would've considered covering in this blog post had I not done the research to recognize HubSpot readers are seeking out that information.
Ultimately, learning key SEO tactics will help you become a writer whose more attuned with your readers' challenges, and ensure you create content that more accurately answers those challenges.
4. Consider how you can attract an audience across a wide variety of platforms.
While SEO is critical for ensuring your content ranks on search engines like Google, it's not the only opportunity for distribution.
To reach a wider audience, it's helpful to learn how to write content that performs well on various platforms such as Instagram, LinkedIn, or email.
Plus, you might be a content writer whose sole job is to write newsletter content or social media copy, depending on your business' needs.
To ensure your content reaches and inspires audiences regardless of the platform they prefer, it's vital you consistently consume content via email and social to pick up writing tips specific for those sources.
5. Incorporate multimedia components to break up the text.
Whenever possible, try to incorporate videos, images, graphs, or other multimedia content to break up the text and make it easier for your readers' to consume — particularly if it's long-form content, like pillar pages or whitepapers.
Consider, for instance, the blog post I wrote: "How to Develop a Content Strategy: A Start-to-Finish Guide".
That blog post is long, with over 3,000 words. To break it up, I embedded videos and other multimedia elements (like blockquotes), to keep the reader engaged throughout.
This is also a good opportunity to increase traffic to your company's various marketing materials. For instance, if you have a new company podcast, try embedding episodes in relevant blog posts to drive listeners to the podcast while providing additional value for your readers — a win, win.
6. Segue into appropriate and relevant calls-to-action.
As a content writer, your job isn't just to create good content (that's what novelists are for). It's also to ultimately convert those readers, listeners, or viewers into prospects and customers.
As such, it's vital you learn how to appropriately include relevant CTAs throughout your content, particularly if those CTAs can help your readers learn more about the topic at-hand.
Consider, for instance, the relevant CTAs embedded in the body text of HubSpot's YouTube video, "How to Understand Facebook Video Insights (Guide)":
 These in-text CTAs direct YouTube viewers to explore other HubSpot offerings, including HubSpot Academy social media courses. The CTAs aren't jarring or off-putting — instead, the content writer did a good job ensuring the CTAs were relevant and truly valuable for the viewer.
These in-text CTAs direct YouTube viewers to explore other HubSpot offerings, including HubSpot Academy social media courses. The CTAs aren't jarring or off-putting — instead, the content writer did a good job ensuring the CTAs were relevant and truly valuable for the viewer.
When you're creating your own content, it's important you ensure you're consistently directing your audience to various business offerings to convert those viewers into prospects and, ultimately, consumers.
7. Edit, edit, edit.
Whenever I finish a first draft of a blog post, I take a few hours off and then return to it at the end of the day. With a fresh perspective, I'm able to edit for small grammatical errors or fix structural issues.
Good content writing is impossible without good content editing.
We're all human and will continue to make mistakes in our writing: That's okay, as long as you remember to go back and edit for those errors, later.
Additionally, small grammatical errors can ultimately make-or-break a readers' trust in your brand as a whole. If they notice you've forgotten periods or misspelled words, they might make the judgment that your content isn't as authoritative and clean as other content on the web, and look for future information elsewhere.
8. Jam-pack value into every sentence.
When I worked with an editor a few years ago, she consistently told me: "If your sentence isn't telling the reader anything new, delete it."
This was a tough pill to swallow. That meant some of my most beautiful, moving sentences needed to be deleted. But it's a fair point: In content creation, you need to move quickly onto your next point, or you'll lose your reader entirely.
Most of your readers are busy people with plenty of distractions, including other businesses' social posts, blog articles, or YouTube videos. Make it easy for them by making your point — and then moving on.
9. Play around with interesting angles.
Good content writers consistently test out new, surprising angles to keep readers engaged and coming back for more.
Consider, for instance, how often "consumer product" has been written about. I'm willing to bet if you've ever researched the topic, you've already seen a wide variety of angles as different content writers try to make an old topic feel new again.
But … have you ever seen consumer product compared to water, before?
Articles like "Be Like Water — A Guiding Principle for Consumer Product" do an excellent job at finding new angles to pull readers' in, even if those readers have seen plenty of consumer product-related content before.
The more unique and surprising your angles are, the more likely you are to capture new audiences.
10. Incorporate original quotes from thought leaders or colleagues to paint a well-rounded argument.
No matter how good my writing is, my readers still don't necessarily want to hear my advice on protecting your mental health while working from home.
Which is why I didn't try to tackle the topic myself — instead, I found a psychologist to provide well-researched, helpful tips to take my piece to the next level.
Even if you're an expert on a topic, consider how you might provide alternative opinions to create a more well-rounded argument. If you're writing a blog post like, "Video vs. Podcast: Which Is Better For Your Business?", see if you can get quotes from both podcasters and video producers (or your own internal colleagues who feel passionate about the subject).
Expert quotes or original insights will impress readers and show them that what they're finding on your website, they won't find elsewhere on the web. And that's powerful.
11. Tell the reader why what you're writing about matters to them and their daily lives.
Let's say you're creating an ebook: "A Comprehensive Guide to Excel".
Not exactly what excited you most when you majored in English, is it?
Imagine how your readers feel: Sure, they might download your ebook if they need the information to excel (ha, ha) in their jobs, but they won't necessarily be excited about it.
Consider, however, how critical Excel is for certain functions. Excel can help a company's financial department analyze year-over-year performance to determine how much budgeting a marketing team will receive in the upcoming year.
That budget contributes to critical growth, and the business' ability to reach and convert new customers. Without it, the marketing team won't be able to increase brand awareness as effectively as they'd like — and the business will suffer, as a result.
When you recognize that Excel can actually be tied to a person's job security, it suddenly becomes much more fascinating, doesn't it?
Content writing isn't just about creating pretty sentences. It's also about telling a reader why a topic should matter to them, and how your content can help them become better in certain areas of their lives — be it work, family, health, or travel. Now that's purposeful.
12. Ground your advice with examples.
As I've covered these content writing tips, I've tried to include a few relevant examples (i.e. my Rel=nofollow blog post).
Examples can help ground your advice and drive a message home — and they can also help demonstrate how readers can apply your advice to their lives.
Particularly when you're writing about loftier, less tangible topics, it's critical you show your readers what you mean, rather than just telling them.
But what better way to demonstrate the importance of examples than to … Show you some examples? (Great segue, huh?)
Let's dive into some examples of powerful content writing, next.
Examples of Content Writing
Along with the examples I've included above, let's take a look at some impressive examples of content writing.
1. Harris and Harris Wealth Management's Blog Post, "What Keeps Me Calm For Clients As Markets Gyrate":

Why It Works
If you have the chance to read the whole article, do — the entire piece is informative and engaging. But what this introduction does particularly well is hook the reader with an opening that's surprising and intriguing.
"You never see it until it happens ... We were due ... I just didn't expect it ..." are all phrases that work to create suspense and encourage the viewer to keep reading. Zaneilia Harris, the author of the post, uses emotion to engage with her readers and make "market downturns" as a topic both personal — and universal. A great example of using a powerful hook to attract, surprise, and delight readers.
2. The Rachel Hollis Podcast, "No Motivation? Here's How to Create Your Own!"

Why It Works
The podcast script is exciting, relevant, and powerful. I found myself nodding along as I listened: something most content writers hope will happen in reaction to their content.
In particular, take a look at the description for the podcast (if you don't have the time to listen to the whole episode): "This week ... Rachel is delivering her best secrets for creating a firestorm of motivation inside a season where even a spark feels hard to find."
The language is compelling and unique — and who doesn't want a firestorm of motivation? This is an excellent example of content writing that encourages a reader to complete a task: In this case, downloading the episode.
3. Trello's Business Plan Template post via LinkedIn.
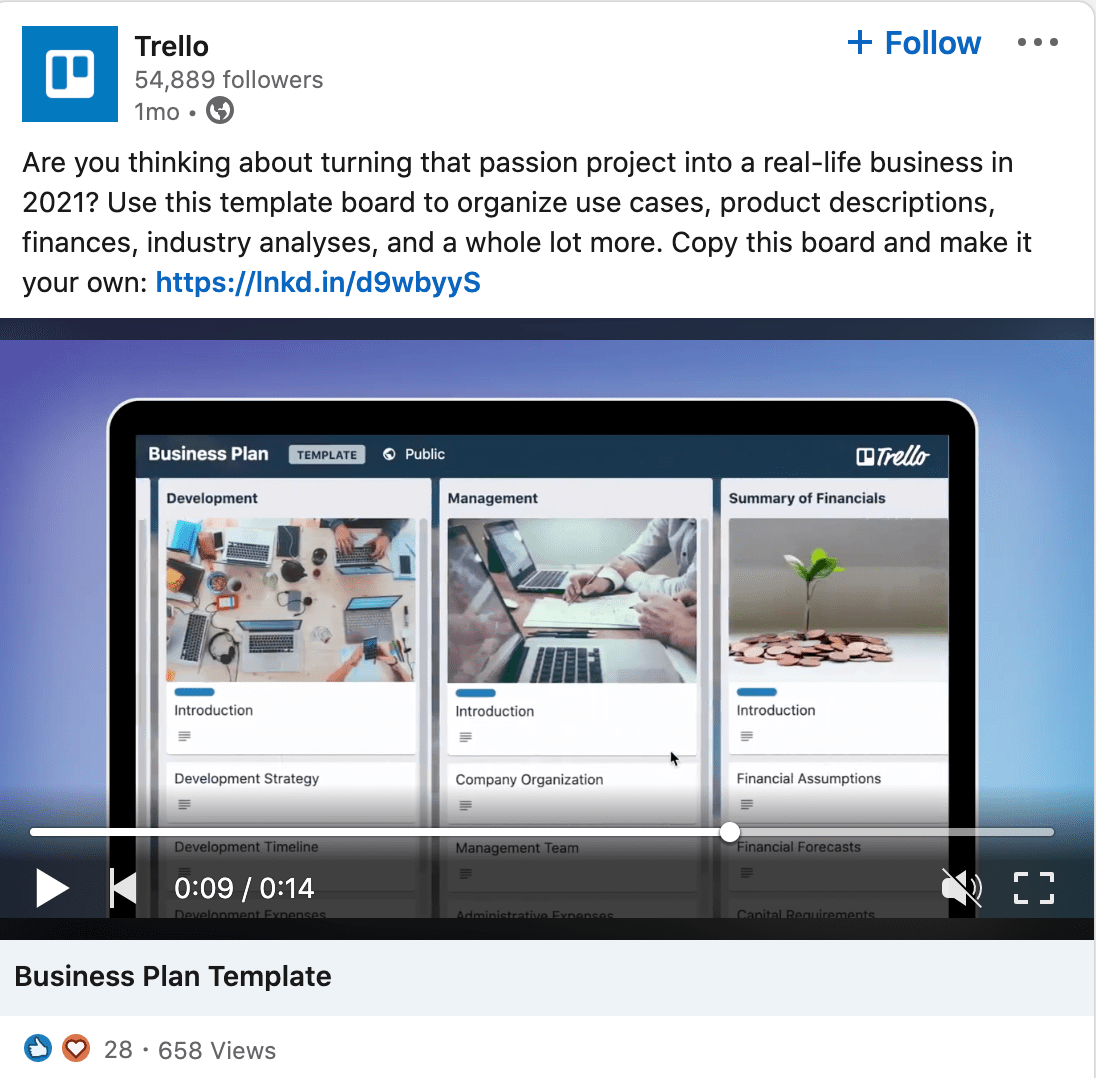
Why It Works
Simply put, sometimes, timing is everything.
Trello's content writers published the right message at the right time —in this case, the very beginning of 2021. Entrepreneurs were likely attracted to the hook, "Are you thinking about turning your passion project into a real-life business in 2021?"
Additionally, the copy uses a wide-variety of examples to attract as many viewers as possible. For instance, the copy mentions the template can help you organize product descriptions, finances, or industry analyses.
Whenever possible, it's helpful to ensure your copy can attract audiences with different challenges or needs — which this post does well.
4. Brian Dean's YouTube video, "How to Start (And Grow) a YouTube Channel in 2020":
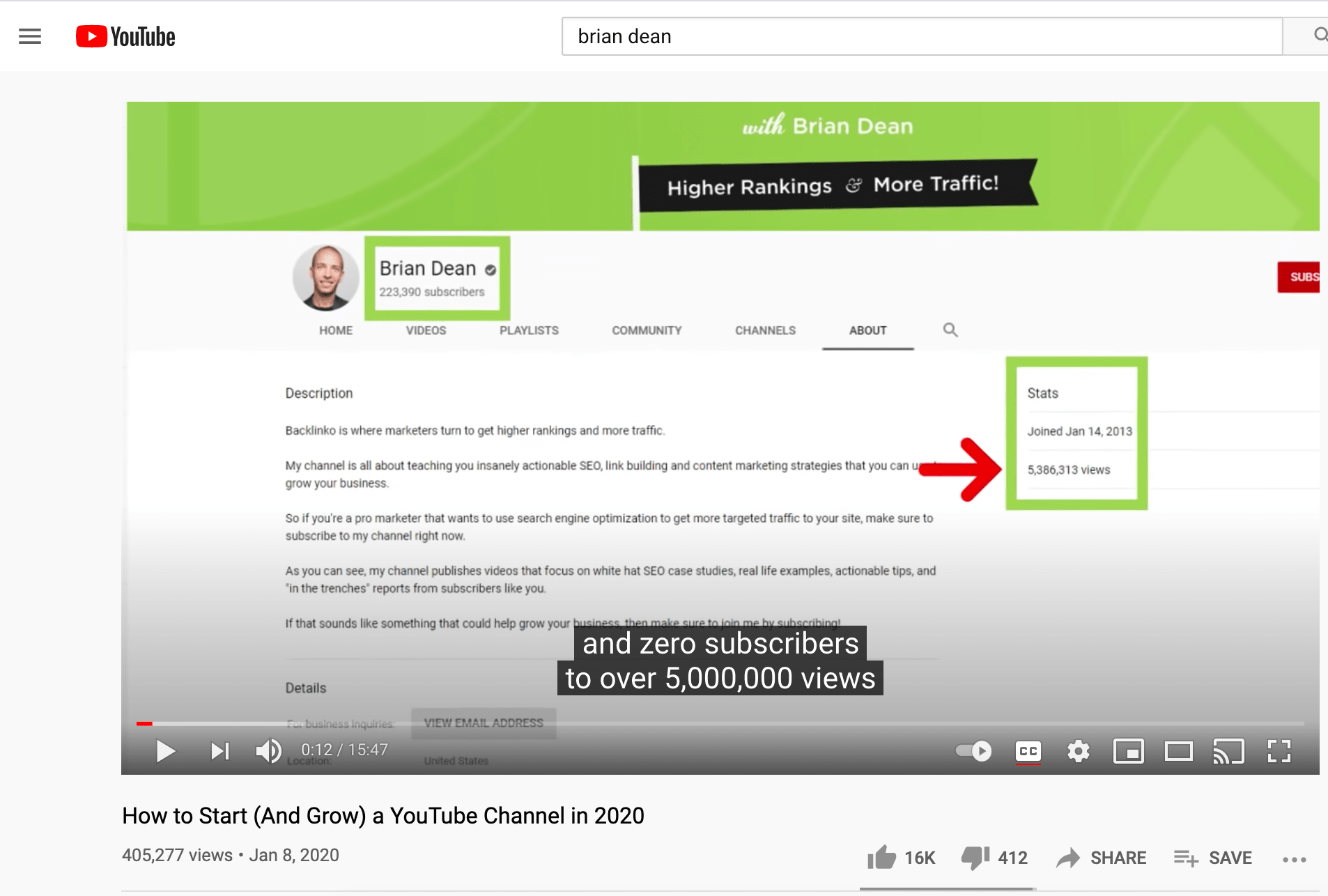
Why It Works
When the video starts, one of the first sentences Brian says is this one: "These are the exact same steps I used to take my channel from zero subscribers to over 5,000,000 views."
That's powerful script writing, and goes a long way towards convincing viewers to keep watching. Why? Because it tells you the content that follows actually helped someone succeed, and creates a level of authenticity that could be missing if Brian simply said, "I've heard from others that these tips work."
5. Ally Bank's "Save for what matters in 2021" newsletter email:

Why It Works
I was immediately drawn to the punny slogan at the top of this email when I opened it in my inbox, which reads: "On your mark. Get set. Goals." The rest of this newsletters packs a punch, too — each sentence is jam-packed with valuable information, and best of all, the content is directed right at me, the reader.
And who doesn't want to make 2021 the "year you save for what matters"?
from Marketing https://blog.hubspot.com/marketing/professional-content-mistakes
When you search for "content writers" on LinkedIn, you're bound to come across an incredibly diverse range of professionals.
For instance, you'll see some content writers create social media copy for small businesses, while others write press materials for insurance brands.
You'll also find that some content writers write long-form editorial content for glamorous magazines, while the more entrepreneurial-type write scripts for their own branded content, like podcast or video.
So, what's going on here ... Are some of them lying?
In fact, they're all telling the truth. Content writing can take various forms, but in essence, it comes down to creating content for digital formats — and (at least in our case) for marketing purposes.
Here, we'll explore what content writing is (hint, hint … I'm currently doing it), as well as tips to take your own content to the next level. Plus, we'll explore examples of incredible, high-quality content writing.
But, to start — What is content writing, anyway?
What is content writing?
Content writing is the process of writing, editing, and publishing content in a digital format.
That content can include blog posts, video or podcast scripts, ebooks or whitepapers, press releases, product category descriptions, landing page or social media copy ... and more.
Simply put, content writers are the storytellers for their brand. They convey meaningful, helpful, and insightful messages to inspire and move an audience to take action — that action being a final sale.
Nowadays, content creation is a critical component of most businesses marketing strategies — in fact, as of 2020, 70% of marketers now actively invest in content marketing.
This means the role of content writer is more in-demand than ever before. However, the role varies depending on both industry and business needs.
For instance, some businesses might invest heavily in a social media strategy, while other companies prefer creating content in the format of blog posts or e-books.
Regardless of format, a content writer is critical for creating high-quality content that represents and strengthens a brand's voice, while attracting, engaging, and delighting the right audience.
When done right, content writing has the power to convert readers into prospects, and prospects into paying customers. So it's undeniably important for your business' bottom-line that you're able to consistently create helpful, engaging content.
But that's easier said than done. To help take your content to the next level, let's dive into some of my favorite content writing tips (these have personally helped me, as well).
12 Content Writing Tips
1. Write unique and original content, and go above-and-beyond what you find online.
Whenever I start a new blog post, like this one, I start with plenty of online research — but that's not where it ends.
After Googling relevant topics, including "content writing tips", I begin creating an outline using some of the information I find online.
However, your piece will never rank if you just copy-and-paste the same information that already exists online — and, even if it does, when your readers catch on (and they will), they'll lose trust in your brand as an authority within the industry.
Once I finish my rough outline (which will include about 60% of the information I found through online research), I fill in the remaining 40% with unique, original insights. If I know about a topic personally (as is the case with "content writing", since I'm a content writer myself), I'll fill in the outline with original anecdotes, tips, or personal examples.
However, if I don't know much about the topic at-hand, that doesn't mean I simply use what's already online. Instead, I'll reach out to internal HubSpotters who are experts on the topic or use other original internal-company resources, or I'll conduct external outreach via my social networks to find a reputable source willing to provide tips, quotes, or original examples to beef up my piece.
Additionally, I'll look for content regarding the topic across a wide range of sources — including YouTube, LinkedIn, Reddit, Quora, as well as podcasts — to ensure when readers' come across my content, it's both comprehensive and unique.
If they can find the same information elsewhere on Google, why should they stay on your page? As a good content writer, it's your job to take your content to the next level, always.
2. Write a good hook to grab your reader's attention.
Sometimes, it's easy to write a good hook — particularly if the topic is intriguing or exciting to you, as the writer.
But what about more boring, mundane topics, like Rel=nofollow?
In certain cases, writing a good hook requires pulling back and looking at the bigger picture. For instance, while rel=nofollow isn't the most fascinating topic (in my opinion), what is interesting to me is SEO, and how SEO can directly impact a company's ability to reach new audiences — plus, how Google has needed to change regulations in recent years due to an increase in illegitimate sites.
Which means, when I started writing 3 Reasons Why SEO's Are Upset About Google's Rel=nofollow Announcement, I used that angle to inspire my hook, and painted a picture: Myself as a Wikipedia editor, writing about zebras, and getting paid $500 to link to a fake news website.
(Now you're interested, aren't you?)
My Creative Writing background helps in this case, and I'm willing to bet your own passion for writing will help you create exciting hooks, as well.
Oftentimes, the introduction and hook is your best opportunity to use your writing skills to truly inspire, move, surprise, and delight your readers from the get-go. Take advantage of that space by thinking: What would make me and my friends want to keep reading?
3. SEO-optimize your content for search engines.
Your writing can be absolutely stunning, but if it's not SEO-optimized, no one will ever read it.
As a content writer, it's critical you become familiar with SEO when it comes to writing.
Being an SEO-savvy writer can help you ensure your content ranks on whichever platforms you're publishing, including YouTube, Google, or even social sites like Instagram.
Plus, you can use SEO to ensure you're writing about the most popular topics related to your products or services, and covering the right sub-topics when you're writing about a given topic.
For instance, "content writing tips" is a keyword phrase I found when conducting keyword research on the topic of "content writing" as a whole — it's not necessarily a sub-topic I would've considered covering in this blog post had I not done the research to recognize HubSpot readers are seeking out that information.
Ultimately, learning key SEO tactics will help you become a writer whose more attuned with your readers' challenges, and ensure you create content that more accurately answers those challenges.
4. Consider how you can attract an audience across a wide variety of platforms.
While SEO is critical for ensuring your content ranks on search engines like Google, it's not the only opportunity for distribution.
To reach a wider audience, it's helpful to learn how to write content that performs well on various platforms such as Instagram, LinkedIn, or email.
Plus, you might be a content writer whose sole job is to write newsletter content or social media copy, depending on your business' needs.
To ensure your content reaches and inspires audiences regardless of the platform they prefer, it's vital you consistently consume content via email and social to pick up writing tips specific for those sources.
5. Incorporate multimedia components to break up the text.
Whenever possible, try to incorporate videos, images, graphs, or other multimedia content to break up the text and make it easier for your readers' to consume — particularly if it's long-form content, like pillar pages or whitepapers.
Consider, for instance, the blog post I wrote: "How to Develop a Content Strategy: A Start-to-Finish Guide".
That blog post is long, with over 3,000 words. To break it up, I embedded videos and other multimedia elements (like blockquotes), to keep the reader engaged throughout.
This is also a good opportunity to increase traffic to your company's various marketing materials. For instance, if you have a new company podcast, try embedding episodes in relevant blog posts to drive listeners to the podcast while providing additional value for your readers — a win, win.
6. Segue into appropriate and relevant calls-to-action.
As a content writer, your job isn't just to create good content (that's what novelists are for). It's also to ultimately convert those readers, listeners, or viewers into prospects and customers.
As such, it's vital you learn how to appropriately include relevant CTAs throughout your content, particularly if those CTAs can help your readers learn more about the topic at-hand.
Consider, for instance, the relevant CTAs embedded in the body text of HubSpot's YouTube video, "How to Understand Facebook Video Insights (Guide)":
 These in-text CTAs direct YouTube viewers to explore other HubSpot offerings, including HubSpot Academy social media courses. The CTAs aren't jarring or off-putting — instead, the content writer did a good job ensuring the CTAs were relevant and truly valuable for the viewer.
These in-text CTAs direct YouTube viewers to explore other HubSpot offerings, including HubSpot Academy social media courses. The CTAs aren't jarring or off-putting — instead, the content writer did a good job ensuring the CTAs were relevant and truly valuable for the viewer.
When you're creating your own content, it's important you ensure you're consistently directing your audience to various business offerings to convert those viewers into prospects and, ultimately, consumers.
7. Edit, edit, edit.
Whenever I finish a first draft of a blog post, I take a few hours off and then return to it at the end of the day. With a fresh perspective, I'm able to edit for small grammatical errors or fix structural issues.
Good content writing is impossible without good content editing.
We're all human and will continue to make mistakes in our writing: That's okay, as long as you remember to go back and edit for those errors, later.
Additionally, small grammatical errors can ultimately make-or-break a readers' trust in your brand as a whole. If they notice you've forgotten periods or misspelled words, they might make the judgment that your content isn't as authoritative and clean as other content on the web, and look for future information elsewhere.
8. Jam-pack value into every sentence.
When I worked with an editor a few years ago, she consistently told me: "If your sentence isn't telling the reader anything new, delete it."
This was a tough pill to swallow. That meant some of my most beautiful, moving sentences needed to be deleted. But it's a fair point: In content creation, you need to move quickly onto your next point, or you'll lose your reader entirely.
Most of your readers are busy people with plenty of distractions, including other businesses' social posts, blog articles, or YouTube videos. Make it easy for them by making your point — and then moving on.
9. Play around with interesting angles.
Good content writers consistently test out new, surprising angles to keep readers engaged and coming back for more.
Consider, for instance, how often "consumer product" has been written about. I'm willing to bet if you've ever researched the topic, you've already seen a wide variety of angles as different content writers try to make an old topic feel new again.
But … have you ever seen consumer product compared to water, before?
Articles like "Be Like Water — A Guiding Principle for Consumer Product" do an excellent job at finding new angles to pull readers' in, even if those readers have seen plenty of consumer product-related content before.
The more unique and surprising your angles are, the more likely you are to capture new audiences.
10. Incorporate original quotes from thought leaders or colleagues to paint a well-rounded argument.
No matter how good my writing is, my readers still don't necessarily want to hear my advice on protecting your mental health while working from home.
Which is why I didn't try to tackle the topic myself — instead, I found a psychologist to provide well-researched, helpful tips to take my piece to the next level.
Even if you're an expert on a topic, consider how you might provide alternative opinions to create a more well-rounded argument. If you're writing a blog post like, "Video vs. Podcast: Which Is Better For Your Business?", see if you can get quotes from both podcasters and video producers (or your own internal colleagues who feel passionate about the subject).
Expert quotes or original insights will impress readers and show them that what they're finding on your website, they won't find elsewhere on the web. And that's powerful.
11. Tell the reader why what you're writing about matters to them and their daily lives.
Let's say you're creating an ebook: "A Comprehensive Guide to Excel".
Not exactly what excited you most when you majored in English, is it?
Imagine how your readers feel: Sure, they might download your ebook if they need the information to excel (ha, ha) in their jobs, but they won't necessarily be excited about it.
Consider, however, how critical Excel is for certain functions. Excel can help a company's financial department analyze year-over-year performance to determine how much budgeting a marketing team will receive in the upcoming year.
That budget contributes to critical growth, and the business' ability to reach and convert new customers. Without it, the marketing team won't be able to increase brand awareness as effectively as they'd like — and the business will suffer, as a result.
When you recognize that Excel can actually be tied to a person's job security, it suddenly becomes much more fascinating, doesn't it?
Content writing isn't just about creating pretty sentences. It's also about telling a reader why a topic should matter to them, and how your content can help them become better in certain areas of their lives — be it work, family, health, or travel. Now that's purposeful.
12. Ground your advice with examples.
As I've covered these content writing tips, I've tried to include a few relevant examples (i.e. my Rel=nofollow blog post).
Examples can help ground your advice and drive a message home — and they can also help demonstrate how readers can apply your advice to their lives.
Particularly when you're writing about loftier, less tangible topics, it's critical you show your readers what you mean, rather than just telling them.
But what better way to demonstrate the importance of examples than to … Show you some examples? (Great segue, huh?)
Let's dive into some examples of powerful content writing, next.
Examples of Content Writing
Along with the examples I've included above, let's take a look at some impressive examples of content writing.
1. Harris and Harris Wealth Management's Blog Post, "What Keeps Me Calm For Clients As Markets Gyrate":

Why It Works
If you have the chance to read the whole article, do — the entire piece is informative and engaging. But what this introduction does particularly well is hook the reader with an opening that's surprising and intriguing.
"You never see it until it happens ... We were due ... I just didn't expect it ..." are all phrases that work to create suspense and encourage the viewer to keep reading. Zaneilia Harris, the author of the post, uses emotion to engage with her readers and make "market downturns" as a topic both personal — and universal. A great example of using a powerful hook to attract, surprise, and delight readers.
2. The Rachel Hollis Podcast, "No Motivation? Here's How to Create Your Own!"

Why It Works
The podcast script is exciting, relevant, and powerful. I found myself nodding along as I listened: something most content writers hope will happen in reaction to their content.
In particular, take a look at the description for the podcast (if you don't have the time to listen to the whole episode): "This week ... Rachel is delivering her best secrets for creating a firestorm of motivation inside a season where even a spark feels hard to find."
The language is compelling and unique — and who doesn't want a firestorm of motivation? This is an excellent example of content writing that encourages a reader to complete a task: In this case, downloading the episode.
3. Trello's Business Plan Template post via LinkedIn.

Why It Works
Simply put, sometimes, timing is everything.
Trello's content writers published the right message at the right time —in this case, the very beginning of 2021. Entrepreneurs were likely attracted to the hook, "Are you thinking about turning your passion project into a real-life business in 2021?"
Additionally, the copy uses a wide-variety of examples to attract as many viewers as possible. For instance, the copy mentions the template can help you organize product descriptions, finances, or industry analyses.
Whenever possible, it's helpful to ensure your copy can attract audiences with different challenges or needs — which this post does well.
4. Brian Dean's YouTube video, "How to Start (And Grow) a YouTube Channel in 2020":

Why It Works
When the video starts, one of the first sentences Brian says is this one: "These are the exact same steps I used to take my channel from zero subscribers to over 5,000,000 views."
That's powerful script writing, and goes a long way towards convincing viewers to keep watching. Why? Because it tells you the content that follows actually helped someone succeed, and creates a level of authenticity that could be missing if Brian simply said, "I've heard from others that these tips work."
5. Ally Bank's "Save for what matters in 2021" newsletter email:

Why It Works
I was immediately drawn to the punny slogan at the top of this email when I opened it in my inbox, which reads: "On your mark. Get set. Goals." The rest of this newsletters packs a punch, too — each sentence is jam-packed with valuable information, and best of all, the content is directed right at me, the reader.
And who doesn't want to make 2021 the "year you save for what matters"?
![→ Download Now: SEO Starter Pack [Free Kit]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/1d7211ac-7b1b-4405-b940-54b8acedb26e.png)